Getty Images
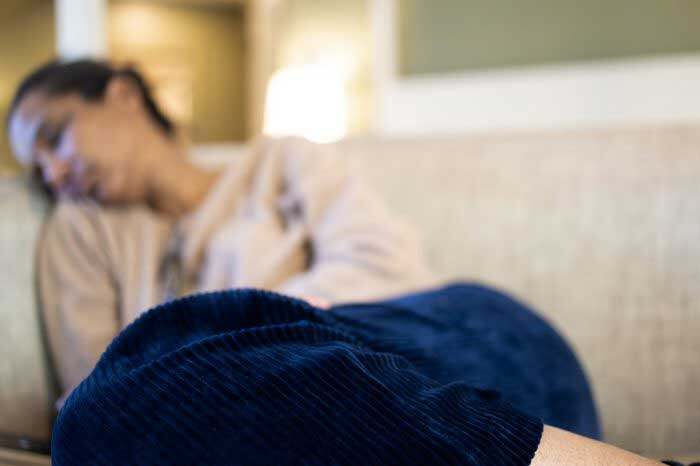
People with long COVID have already fought hard to become visible.
The assertion from Queensland’s chief health officer John Gerrard that it’s time to stop using the term “long COVID” has made waves in Australian and international media over recent days.
Gerrard’s comments were related to new research from his team finding long-term symptoms of COVID are similar to the ongoing symptoms following other viral infections.
But there are limitations in this research, and problems with Gerrard’s argument we should drop the term “long COVID”. Here’s why.
A bit about the research
The study involved texting a survey to 5,112 Queensland adults who had experienced respiratory symptoms and had sought a PCR test in 2022. Respondents were contacted 12 months after the PCR test. Some had tested positive to COVID, while others had tested positive to influenza or had not tested positive to either disease.
Survey respondents were asked if they had experienced ongoing symptoms or any functional impairment over the previous year.
The study found people with respiratory symptoms can suffer long-term symptoms and impairment, regardless of whether they had COVID, influenza or another respiratory disease. These symptoms are often referred to as “post-viral”, as they linger after a viral infection.
Gerrard’s research will be presented in April at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. It hasn’t been published in a peer-reviewed journal.
After the research was publicised last Friday, some experts highlighted flaws in the study design. For example, Steven Faux, a long COVID clinician interviewed on ABC’s television news, said the study excluded people who were hospitalised with COVID (therefore leaving out people who had the most severe symptoms). He also noted differing levels of vaccination against COVID and influenza may have influenced the findings.
In addition, Faux pointed out the survey would have excluded many older people who may not use smartphones.
The authors of the research have acknowledged some of these and other limitations in their study.